- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
What is the swing trading?
Swing trading is a short-term investment strategy where investors buy and hold an asset for a short period, typically a few days to several weeks, with the aim of generating profit.
Definition
Swing trading is a short- to medium-term investment strategy where traders hold positions for a longer duration, unlike day trading, which involves rapid buying and selling.
Methodology
• Time Frame
Swing trades are trading sessions that last for several weeks or a couple of months, with some extending beyond a couple of months.
• Technical Analysis
Swing traders utilize technical analysis to identify patterns, entry points, and potential price movements, utilizing charts, trends, and patterns to make informed decisions.
• Risk/Reward Ratio
Swing traders use a risk/reward ratio to determine entry points, place stop-loss orders, and anticipate profit exits, ensuring successful swing trading.
• Fundamental Analysis
Technical analysis is the primary tool used in swing trading, but some traders also employ fundamental analysis to assess the asset's potential for improvement.
Advantages and Disadvantages
• Advantages
Profit Potential
Swing trading enables traders to profit from anticipated price changes without committing to long-term positions.
Flexibility
Swing traders can effectively navigate market fluctuations and capitalize on short- to medium-term trends.
Risk Management
Swing traders effectively manage risk by setting stop-loss orders and profit targets.
• Disadvantages
Overnight and Weekend Risk
Swing trading is a trading strategy that involves trading overnight or weekend sessions, which can lead to price gaps.
Market Volatility
Extreme volatility can result in unexpected outcomes, such as rare intraday swing trades.
Short-Term Focus
Swing trading is a trading strategy that focuses on short-term movements, which may not be suitable for all investors.
Swing trading is an active trading strategy that combines technical analysis with intermediate-term opportunities, aiming to profit from anticipated price moves while minimizing risk.
What are some popular swing trading strategies?
Some popular swing trading strategies are utilized by traders to capture short- to medium-term price movements.
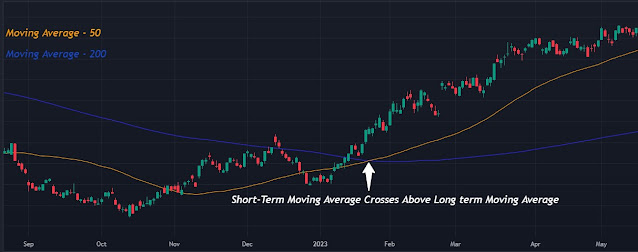
01. Moving Average Crossover
• Concept
The strategy employs the use of two moving averages, typically short-term and long-term, to detect potential trend reversals.
• Execution
# A potential bullish trend occurs when the short-term moving average (50-day) crosses above the long-term moving average (200-day), indicating a positive trend.
# A potential bearish trend is indicated when the short-term moving average crosses below the long-term moving average.
• Example
Traders may buy when the 50-day moving average crosses above the 200-day moving average and sell when the opposite crossover occurs.
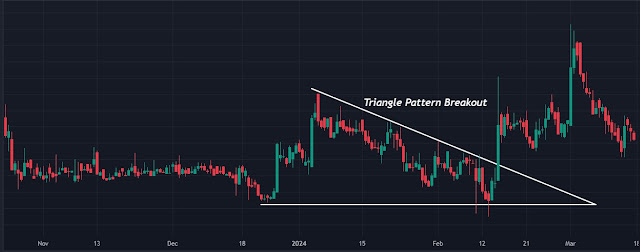
02. Breakout Trading
• Concept Trading
Breakout traders identify price levels where an asset breaks out of a defined range or pattern.
• Execution
# Identify a consolidation phase, such as a sideways channel or a triangle pattern.
# When the price exceeds the upper limit, it is advisable to consider going long.
# When the price falls below the lower boundary, it is advisable to consider going short.
• Example
A stock trading in a tight range suddenly breaks out to the upside, triggering a buy signal.
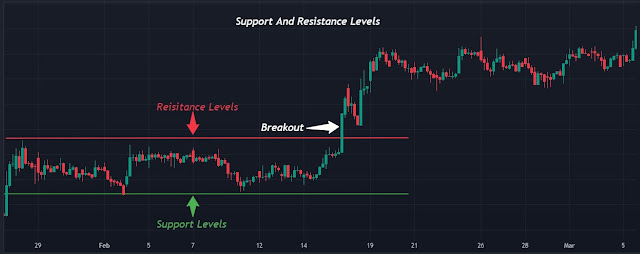
03. Support And Resistance Trading
• Concept
Swing traders make trading decisions by focusing on key support and resistance levels.
• Execution
# Invest near strong support levels, where prices typically increase, as they are historically a good place to buy.
# The text advises selling or shorting near strong resistance levels, where historically prices reverse.
• Example
When a stock approaches an established support level, traders may buy with a stop-loss below that level.
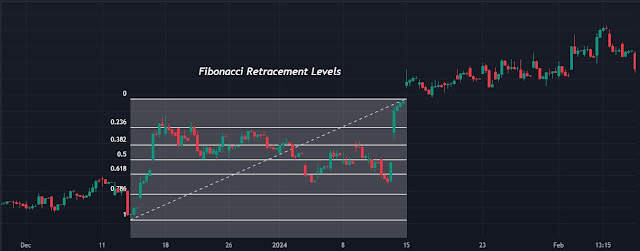
04. Fibonacci Retracement
• Concept
Fibonacci retracement levels are utilized to identify potential reversal points following a significant price shift.
• Execution
# The task involves plotting Fibonacci retracement levels on a chart, typically 38.2%, 50%, and 61.8%.
# The text suggests observing price reactions at specific levels.
• Example
If a stock retraces to the 50% Fibonacci level and shows support, traders may consider a long position.
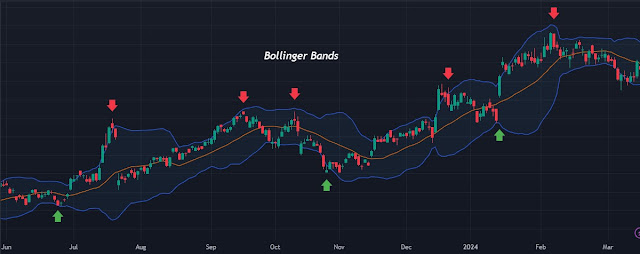
05. Bollinger Bands
• Concept
Bollinger Bands are a type of moving average that includes two standard deviation bands.
• Execution
# When the price reaches the lower band, it may indicate an oversold condition, indicating a potential buy.
# When the price reaches the upper band, it may indicate an overbought condition, indicating a potential sell.
• Example
Traders are actively monitoring for price reversals near the bands.
Risk management is crucial for success, requiring adaptation to risk tolerance, time frame, and market conditions, with due diligence and combining technical and fundamental analysis for better decision-making.
What is some common mistake to avoid in swing trading?
To increase your chances of success in swing trading, it's essential to avoid common mistakes.
01. Ignoring Risk Management
• Mistake
The issue can be resolved by setting stop-loss orders or minimizing the capital risk on a single trade.
• Solution
Stop-loss orders are a crucial tool in trading, allowing traders to limit their losses by setting a specific risk per trade.
02. Chasing the Market
• Mistake
The term "trading" refers to the act of entering a trade after a significant price change has already occurred.
• Solution
To maximize your chances, wait for pullbacks or retracements to better entry points and avoid the fear of missing out (FOMO).
03. Overtrading
• Mistake
Overspending on trading without a clear strategy.
• Solution
Selectively focus on quality setups rather than quantity, prioritizing quality over quantity.
04. Lack of Patience
• Mistake
The act of prematurely exiting a trade due to impatience.
• Solution
To achieve success, set achievable profit targets, adhere to your strategy, and avoid making emotional decisions.
05. Ignoring Market Conditions
• Mistake
The statement is not taking into account the current market trends or news events.
• Solution
It is crucial to comprehend the broader market context and to align with trends, rather than opposing them.
06. Not Adapting to Changing Conditions
• Mistake
Continually employing the same strategy despite market fluctuations or alterations.
• Solution
After a losing trade, take a break and analyze the situation before re-entering the market.
07. Revenge Trading
• Mistake
The individual is actively seeking to recover losses by immediately entering another trade.
• Solution
After a losing trade, take a break and analyze the situation before re-entering the market.
08. Neglecting Fundamental Analysis
• Mistake
The statement is a summary of a statement that criticizes a company for relying solely on technical analysis without considering its fundamentals.
• Solution
The text suggests a comprehensive view by combining technical and fundamental analysis.
09. Overleveraging
• Mistake
Excessive leverage, particularly with small accounts, is a significant issue.
• Solution
It is recommended to keep a comprehensive trading journal to document your trading activities, both successes and failures.
10. Not Keeping a Trading Journal
• Mistake
The issue is not accurately tracking your trades, strategies, and emotions.
• Solution
It is recommended to keep a comprehensive trading journal to document your trading activities, both successes and failures.
How do i develop a swing trading plan?
Continuous learning is crucial for enhancing swing trading outcomes by avoiding common pitfalls and fostering discipline and adaptability.
A successful swing trading plan is crucial for consistent results, and following these key steps is essential.
01. Understand Your Trading Style
• Choose your preferred trading style, which includes swing trading, which falls between day trading and long-term investing, and decide whether to focus on short- to medium-term trades.
• The analysis should take into account factors such as risk tolerance, time commitment, and available capital.
02. Define Your Goal
• The text emphasizes the importance of clearly outlining trading objectives, such as capital growth, income, or a specific percentage return, when using swing trading.
• Establish achievable and quantifiable objectives.
03. Choose Your Time Frame
• Determine the duration of your swing trades, which typically ranges from a few days to several weeks.
• Part-time traders may find longer time frames more suitable, while shorter time frames necessitate more active monitoring.
04. Choose Your Trading Instruments
• Swing trading involves trading various assets such as stocks, forex, commodities, or cryptocurrencies.
• Gain a comprehensive understanding of the characteristics and volatility of your chosen instruments.
05. Technical Analysis
• Examine price charts, patterns, and indicators to identify trends, support, and resistance levels.
• Utilize tools such as moving averages, Bollinger Bands, and Fibonacci retracements to make informed decisions.
06. Risk Management
• Determine your risk per trade by determining the amount of capital you are willing to invest in each trade.
• Set stop-loss orders to limit potential losses and never take on more than you can afford to lose.
07. Entry And Exit Strategies
• Entry points (buy) and exit points (sell).
• Wtach breakout levels, moving average crossovers, or candlestick patterns for entries.
• Exit when your target is reached, or trade goes against you.
08. Position Sizing
• The position size should be determined by considering your risk tolerance and stop-loss level.
• Maintain consistent position sizes to avoid overleveraging.
09. Trading Routine
• Develop a daily routine, decide when to analyze charts, monitor news, and execute trades.
• Maintain your strategy even in the face of fluctuating market conditions.
10. Review And Adapt
• Maintain a trading journal to track your trades, decisions, emotions, and outcomes, and regularly assess your trades.
• Gain insights from both successful and unsuccessful trades and adjust your strategy accordingly.
Consistency and discipline are essential in swing trading, as a well-structured plan helps maintain focus, manage risk, and enhances success chances.
How do i develop trading plan?
Backtesting is a crucial method for assessing the effectiveness of a swing trading strategy by simulating its historical performance under specific rules.
01. Collect Historical Data
• To trade an asset, obtain historical price data from platforms like Yahoo Finance, TradingView, or specialized backtesting tools.
• The data should be collected over a suitable time frame, such as several years, to accurately represent the diverse market conditions.
02. Choose Backtesting Platform or Software
• Utilize a backtesting tool or software that enables you to apply your strategy to historical data.
• Popular backtesting platforms include Amibroker, QuantConnect, and TradingView.
03. Define Your Strategy Rule
The specific rules for your swing trading strategy should include:
• Entry conditions (when to buy or short).
• Exit conditions (when to sell or cover).
• Stop loss levels
• Profit targets
• Any other relevant criteria.
04. Apply Your Strategy to Historical Data
• The program allows users to manually simulate trades based on their strategy rules using historical price data.
• The task involves recording the entry and exit points of each trade, along with the relevant parameters.
05. Evaluate Prformance Matrics
The task involves determining key performance metrics for backtested trades.
• Profit and Loss (P&L): refer to the total gains or losses a company experience.
• Win rate: refers to the percentage of successful trades.
• Risk-Adjusted Return: is calculated by adjusting the risk per trade.
• Maximum Drawdown: refers to the largest decline from peak to trough.
• Sharpe Ratio: The risk-adjusted return is a measure of an investment's return in relation to its volatility.
• Expectancy: The average profit per trade is a measure of the overall profit generated by a trader.
The effectiveness of the strategy can be evaluated by comparing these metrics.
06. Validate Against market Conditions
• It is crucial to ensure that your backtesting strategy is suitable for various market phases, including bull markets, bear markets, and sideways trends.
• Adjust your strategy if it performs poorly under specific conditions.
07. Refine and Optimize
The strategy should be refined based on the backtesting results.
• Entry or exit rules should be modified.
• Position sizing should be adjusted.
• Optimizing the parameters, if any, if applicable.
The strategy should be continuously enhanced based on historical performance.
Backtesting offers historical performance insights, but real-world execution may vary due to slippage, liquidity, and other factors. Regularly review and update your strategy as market conditions change.
Thanks For Reading! Bullish Ticks
Follow Us: X
Comments
Post a Comment